How to Manually Repair Windows 7 Boot Loader Problems
If you’re having boot problems on your Windows PC, it’s often helpful to repair the MBR (Master Boot Record) to restore the Windows 7 boot loader—and you can do it easily from the Windows installation disc.
This is generally most useful if you’ve broken something and there’s a boot loader error, or if you have made the mistake of installing an older version of Windows on the same PC that already has Windows 7 which wipes out the boot loader.
Note: If your PC starts booting into Windows but fails, you should probably try using Safe Mode instead.
Boot From the Windows Install Disc
The first thing you’ll need to do is boot off the install disc, and then click through until you see the “Repair your computer” link in the lower left-hand corner.

You’ll need to choose the correct installation of Windows and then click the Next button.

And then you’ll get to the System Recovery Options screen, where you can get to the Command Prompt.
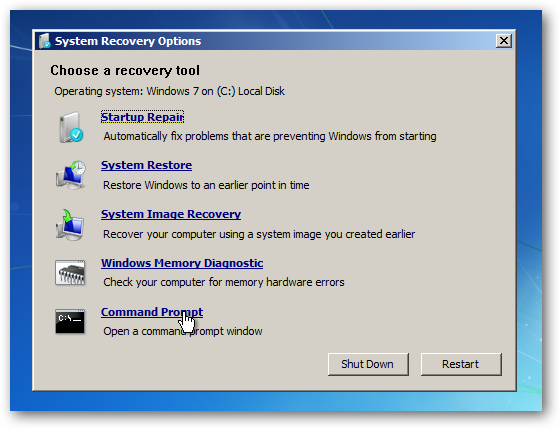
Repairing the Master Boot Record
If you want to restore the master boot record, you can simply type in the following command:
bootrec /fixmbr
You can also write a new boot sector onto the system partition with this command (which is often more useful):
bootrec /fixboot
And of course, if you just use bootrec /? you’ll be able to see all the options.

This is the same way that we fixed the “BOOTMGR is missing” error when trying to boot up Windows 7 or Vista.
Replacing the Windows XP Bootloader with Windows 7
If you’ve managed to install XP on the same PC that you already had Windows 7 on, you’ll noticed that you can’t boot into Windows 7 anymore. You can use this command to fix that and restore the Windows 7 bootloader:
bootsect /nt60 all
Depending on the partition that you’ve installed, you might need to substitute the drive letter instead of “all”.

Note: if you want to restore Windows XP back to the menu, you can open up a command prompt in Windows 7 and run this command:
bcdedit /create {ntldr} -d “Windows XP”

Using the Automated Startup Repair
Of course, all this command-line stuff is probably not necessary in most cases. You can usually just use the Startup Repair option from the Recovery menu…

It’ll check for problems and probably fix them. If not, then you can always use the command prompt.

Have you ever needed to restore your boot loader to get Windows working again?











