Re-Partition Your Hard Disk Without Losing Data With EASEUS Partition Manager:
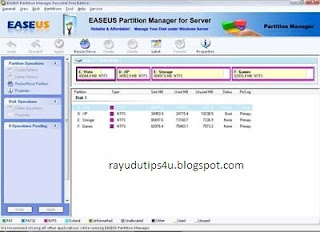
Hard disk is place where to keep all data and information within the computer, it’s good to separate and keep the data in hard disk by partition. Normally most of the users will partition their hair disk to two partitions (OS and Data), this is to ensure all their data still remain in the hard disk while their operating system partition corrupted. For those hard disk where no have partition, all the data are keep together with the operating system, and there is a risk hard to recover their data when operating system was corrupted and cannot boot-in to the windows. To prevent this happen, now users can use EASEUS Partition Manager Home Edition.
What is EASEUS Partition Manager ?
EASEUS Partition Manager Home Edition is free comprehensive hard disk partition management software to let you enjoy free with all the powerful functions: Resize and Move partitions, Create, Deleteand Format partitions, Hide and Unhide partitions and much more. What’s more, the freeware works perfectly with hardware RAID and Windows 2000/XP/Vista Operating Systems. Your data is completely protected during all operations. Its great free tool that users can use to re-partition hard disk rather use other partition software where need pay for the license.
Features of EASEUS Partition Manager:
- Support hardware RAID.
- Resize and move partitions without losing data.
- Create, delete and format partitions with simple step.
- Label partitions – assigned to a partition for easier recognition.
- View Disk/Partition property of each partition.
- Hide and unhide partitions – protect important data from unauthorized or casual access.
- Set an active partition – specify one partition to be the boot partition.
- Powerful safety features protect you against system failures while partitioning.
- Step-by-step wizard walks you through partitioning process.
- Preview any partitioning tasks before completing it.
- Change cluster size automatically and manually.
- Undo feature any partition step.
- Support hard disks from 2 GB to 1 TB.
- User-friendly interface.











 Back to the top
Back to the top